Lake Facts
| Lind/Nottage | |
|---|---|
| DNR ID | MN 03-0376-00(Lind) MN 03-0372-00(Nottage) |
| Township(s) | Lake View |
| Lake Classification | Natural Environment |
| Ordinary High-Waterline (OHW) | N/A |
| Size | 45 Acres (Lind) 71 Acres (Nottage) |
| Maximum Depth | 51 Ft (Linda) 25 Ft (Nottage) |
| Watershed Area | 599 Acres |
| Impairment Listings | none |
| Common Fish Species | Black crappie, Bluegill, Northern pike, Pumpkinseed, Walleye |
| Invasive Species | Curly-leaf pondweed (Lind) |
| Public Access/Beaches | none |
| Land Use | 17.4% Open Water 7.5% Developed 11.7% Wetlands 17.2% Cultivated Crops 16.8% Forest 29.5% Grassland |
Map
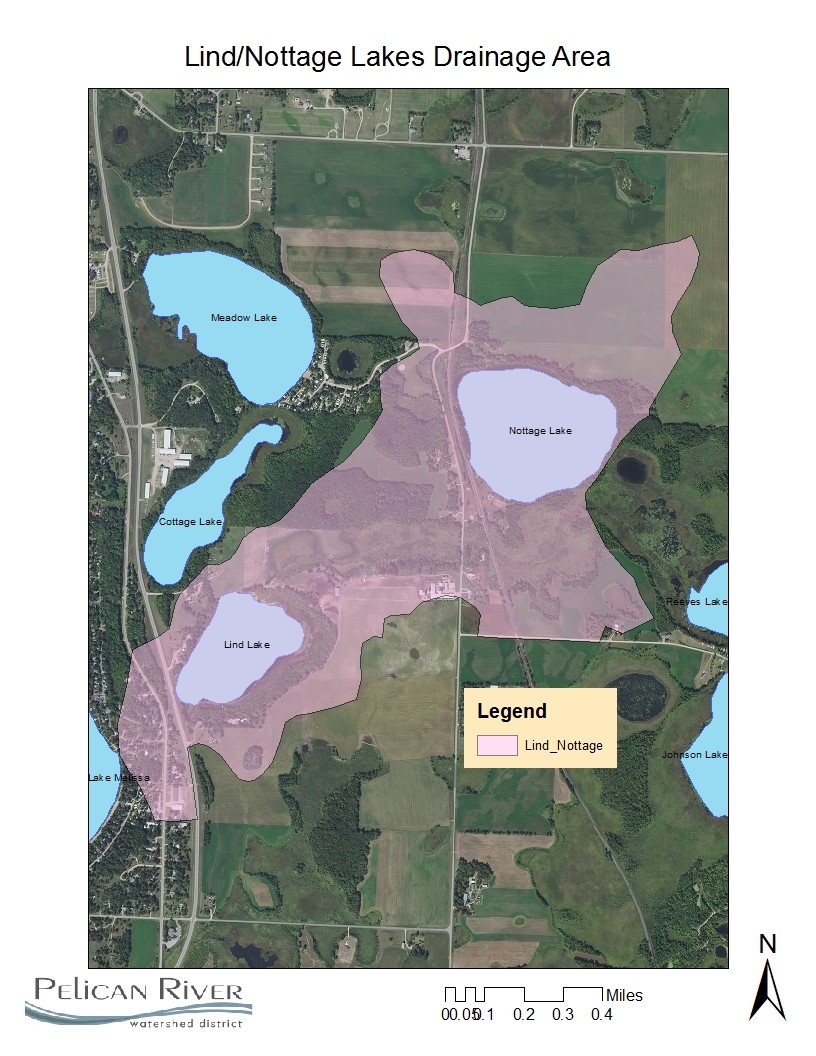
Lake Description & Overview
Lind and Nottage Lakes are both small natural environment lakes located in the drainage area between Johnson/Reeves Lake and Lake Melissa.
Nottage Lake is located in the northern portion of the drainage area with no residential development. There are no surface water inputs to the lake other than stormwater runoff from primarily cultivated cropland. A 100 ft forested buffer is located between agricultural uses. Because there is no residential development on the lake and it is disconnected from major public watercourses, water quality sampling has never been conducted.
Lind Lake is located in the southern portion of the drainage area. Water flows into the north side of the lake via a wetland stream from Reeves Lake. A small stream exits the lake to the south and flows to Lake Melissa. Lind is deep for its size, reaching a depth of 51 feet in the northern portion of the lake. There are currently four single family residential homes along the western shoreline and one commercial business on the south shore. Heavy agricultural use is present, including cattle grazing within 150 feet of the lake, and using the input stream as a water source.
In 2015, water quality monitoring began in Lind to obtain baseline data and investigate nutrient loads to Melissa. The proximity of cattle to the lake and stream raised concerns about nutrients loads. Results from monitoring showed in-lake mean summer nutrient levels at 42ppb, putting the lake in the mildly eutrophic category. Interestingly, phosphorus levels were at their highest in the spring and declined in the summer. Water clarity also increased in the summer as the lake stratified. Anoxia developed below 3 meters in June and remained throughout the year. Internal phosphorus loading is a major factor with bottom orthophosphate concentration approaching 1300 ppm in September. Monitoring of nutrient load from Lind to Melissa was minimal due to low stream flow.
Water Quality
Lind
Learn More
DNR Lakefinder
Get information on water levels, fish stocking, and water clarity for Lind and Nottage.
MPCA Surface Water Data
Find historical lake and stream water quality data for Lind.
Goals
Short Term Goals – Year 2025
- Maintain a 5-year mean summer phosphorus concentration at or below 40 μg/L ± 4%
- Maintain mean summer Secchi depth no less than 8 ft
Long Range Goals – Year 2035
- Maintain a 5-year mean summer phosphorus concentration at or below 40 μg/L ± 4%
- Maintain mean summer Secchi depth no less than 8 ft
Studies & Surveys
Future Surveys as part of 2020-2030 Monitoring Plan
Water Quality- (Lind) 2028
Past Surveys
Water Quality (Lind)– 2015, 2018, 2023
For more studies and surveys, see the Detroit-Rice Water Management Area.

